This is a simple app for managing SystemD services. It supports all Linux distributions based on Debian, Ubuntu, Arch Linux, and Fedora.
Managing Services
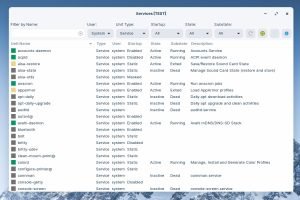
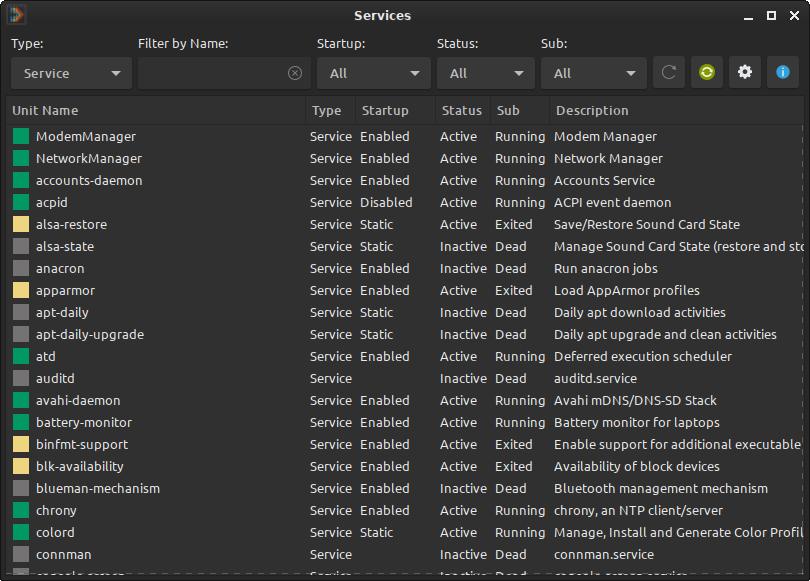
You can use this app to view and manage system services.


The Startup column indicates if the service will start automatically at system boot. You can right-click and Disable the service to prevent it from starting automatically. For example, if you don’t use printers you can disable the cups service.
Even if you disable a service, it can still run if it is required by other services, and if it is started by an application. For example, the cups service that is disabled may be started by LibreOffice when you try to print a file. To prevent the service from running under any circumstances, right-click and Mask the service. Masking a service will disable it completely.
To enable the service again, right-click and Unmask the service. After it is unmasked, right-click and Enable the service.
Analyze boot time
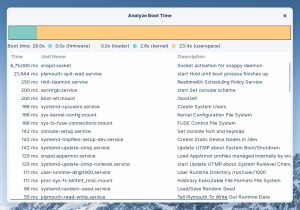
Click the “Analyze boot time” button to display the time taken by services during boot.

- Firmware indicates the time taken by UEFI BIOS
- Loader indicates the time taken by the bootloader
- Kernel indicates the time taken by the Linux kernel
- Userspace indicates the time taken by system services.
The Time column displays the time taken by each service to complete. Services are listed in order of execution time. Services that run at boot often run in parallel, so if you add up the execution time for all services it will be more than the userspace time.
For example, the service NetworkManager-wait-online is at the top of the list with an execution time of 30 seconds but has little impact on boot time. This service simply waits for the internet connection to come online and exits after waiting for a maximum of 30 seconds.
Most of these services are important and should not be disabled. Doing so can break your system and prevent it from starting. If you wish to disable any services, please do so at your own risk.